Basics of protein
The musculature of the human body consists mainly of water and proteins. Furthermore, proteins play an important role in many bodily functions go 언어. Muscle, skin, hair, organs, and enzymes are built upon a specific protein basis and sequence of amino acids in the body. In addition, they are also needed for the synthesis of hormones (signal substances) and neurotransmitters (messenger substances in the brain and central nervous system) 다운로드. For this reason alone, it makes sense to provide the body with a sufficient amount of protein. Only if the essential amount of the required protein intake is met and there is a positive nitrogen* balance in the body, you will be able to build new muscle tissue is 새 신발 다운로드. Or more simply put: No protein – No muscles!**
It should be noted, however, that the human body and physiology is not capable of storing proteins in advance, as it is possible with fats or carbohydrates ccm mp3 다운로드. Therefore, there has to be a constant intake of proteins and amino acids via food. If this does not happen, the body begins to consume its own protein in the form of muscles after a certain period of time 다운로드. Losing muscle mass not only means a less muscular look but also a drop in physical performance.
However, proteins supplied with food cannot be directly processed by the body, meaning just because you eat a pound of chicken breast doesn’t mean that that pound goes directly into your biceps muscle 다운로드. Moreover, protein must first be broken down by the digestive system into its components, the amino acids. It should be obvious by now that protein is made up of a specific sequence of multiple amino acids; different combinations of amino acids equal a different protein, enzyme, hormone, etc 선수무적 다운로드. Scientifically we differentiate between 8 essential and 12 nonessential amino acids. The essential amino acids however, are those that must be supplied to the body in any case, because it cannot produce them by itself at all or in sufficient quantity 다운로드. These essentia
l amino acids are the following:
- Isoleucine
- Leucine
- Lysine
- Methionine
- Phenylalanine
- Threonine
- Tryptophan
- Valine
Isoleucine, leucine and valine play a special role here 다운로드. They are also referred to as branched chain amino acids (BCAAs) and make up ca. 35% of the human musculature.
Similarly, the non-essential amino acids are those that the body itself can assemble from the essential amino acids:
- Alanine
- Arginine
- Asparagine
- Aspartic acid
- Cysteine
- Glutamine
- Glutamic acid
- Glycine
- Histidine
- Proline
- Serine
- Tyrosine
During digestion, the body splits the protein in the food into individual amino acids, which are then absorbed into the bloodstream and are thus available for building up body proteins (e.g 고서이. muscles). The scientific term for building or rebuilding protein is called “Muscle protein (bio)synthesis”.
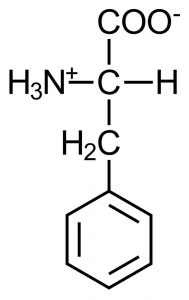
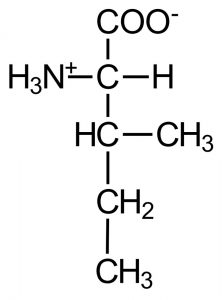
* Nitrogen is a chemical element found in proteins and amino acids (see chemical structures)
**Specific (non-essential) amino acids can be synthesized by the body from carbohydrates and fats through biochemical pathways (e.g. transamination of pyruvate for production of alanine)
Sources: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3381813/